May 7, 2015
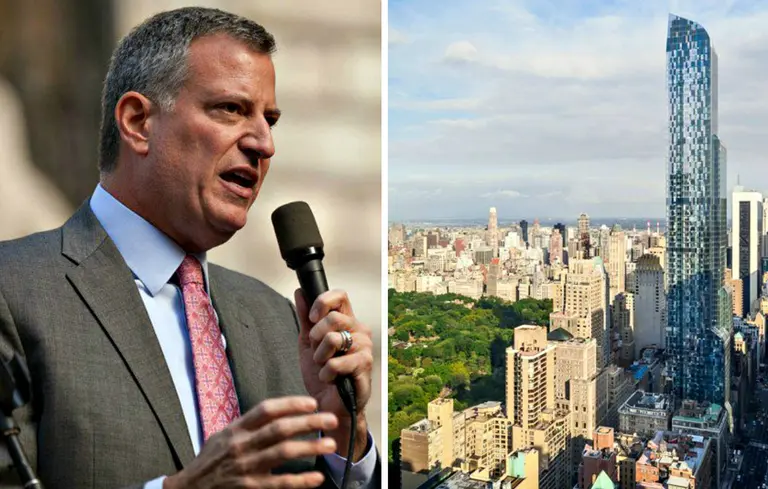
From the onset, Mayor de Blasio has been extremely vocal about his plan to add 200,000 units of affordable housing over 10 years, 80,000 of which will be new construction. Though many feel this is an arbitrary number, backed up by no data as to where the units will be, the Mayor seems committed to reforming current policies to reach his goal. And after months of speculation, he has revealed his planned changes to the city's 421-a tax incentive program, which is set to expire in June.
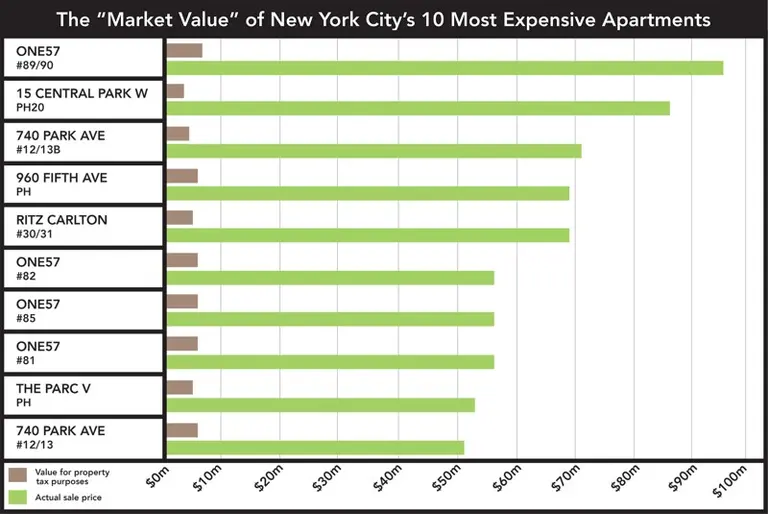
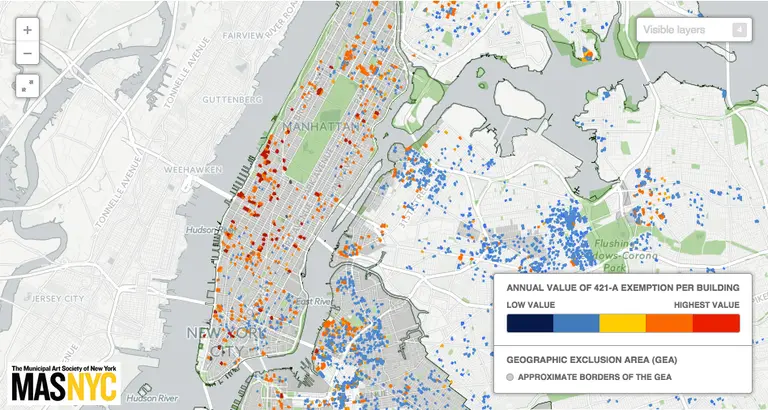
According to the Times, under his proposal, the controversial tax would no longer apply to condo projects (to understand the logic behind this decision just look at the $100 million sale at One57 that received the tax abatement). But it would apply to new rental projects, which would have to have apartments for poor and working-class residents make up 20 to 30 percent of the building in order to qualify for city tax breaks. It would also extend the abatement from 25 years to 35 years. Another part of the overhaul is to eliminate so-called poor doors.
De Blasio also wants to up the city's mansion tax. Currently, home sales over $1 million are subject to a 1 percent tax, but de Blasio proposes adding an additional 1 percent tax for sales over $1.75 million, as well as a third 1.5 percent tax for sales over $5 million. He estimates this will bring in an extra $200 million a year in tax revenue, money that would be allocated to affordable housing programs.
More details ahead